Decarbonization how do european automakers deal with EU emissions standards?

The automotive field has been facing up ecological transition for years now. The EU has set a target for 2030 of reducing net greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% compared to levels in 1990. European automakers are taking a range of actions to support decarbonization efforts and reduce the carbon footprint of their vehicles. By investing in electrification, alternative fuels, lightweight materials, sustainable manufacturing, and carbon offsetting, they are helping to drive the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
All the measures to reach a unique goal
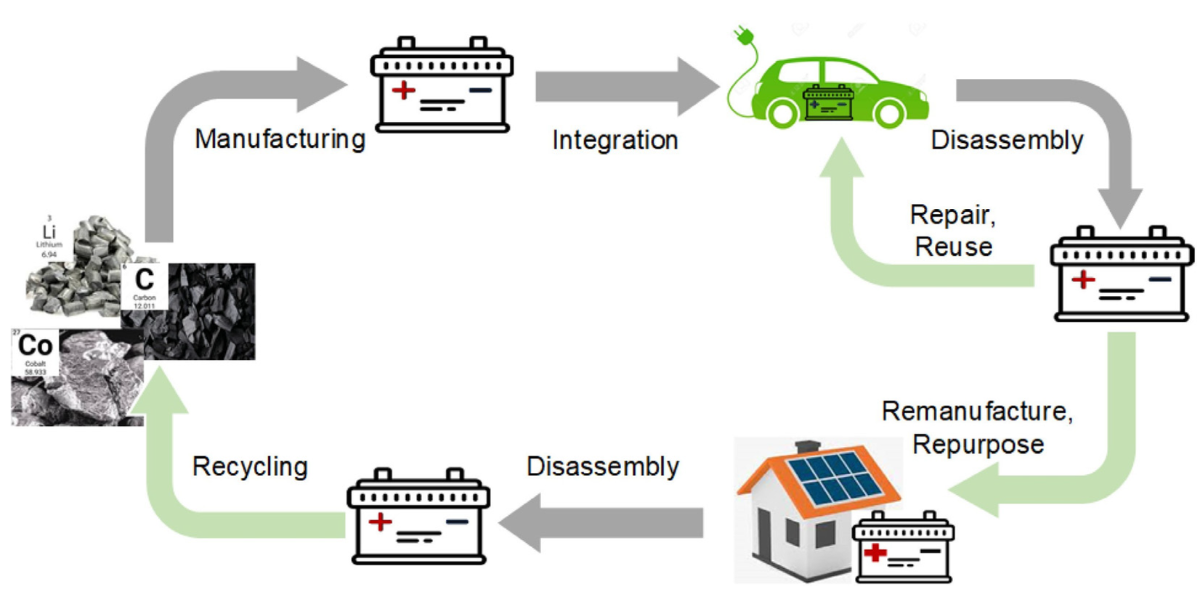
Electric - Many European automakers are investing heavily in the development and production of electric vehicles (EVs) and (plug-in) hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). This shift towards electrification is a key strategy for reducing their vehicles’ carbon emissions. Electricity is one of the main fuels being used for decarbonization, particularly for the electrification of transportation and the generation of renewable energy. Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular as battery technology improves and charging infrastructure expands, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind are increasingly being used to generate electricity. They produce no emissions from the tailpipe, and when powered by renewable energy sources, they can be a zero-emissions solution for transportation.
Hybrid vehicles use a combination of an electric motor and a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The electric motor assists the ICE during acceleration and at low speeds, and regenerative braking is used to recharge the battery.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) are similar to hybrid vehicles but have a larger battery that can be charged from an external source, such as a charging station or a wall outlet. This allows them to travel a certain distance on electric power alone before switching to the ICE.